With World Physiotherapy Day coming up on 8 September we’re sharing our thoughts on the topic they’re highlighting this year: “the role of physiotherapy and physical activity in healthy ageing”.
In 2025, the focus is on healthy aging, with a special emphasis on preventing falls and maintaining strength in older adults. The stats show that falls are a leading cause of injury and loss of independence in later life, yet many are preventable through targeted exercise, balance training, and education – all core areas of physiotherapy.
This day is an opportunity to raise awareness, share knowledge, and inspire action to help people of all ages move better and live well.
Falls And Ageing
Falls might seem like no big deal, but they can be serious – especially for older adults. In fact, falls were the leading cause of injury hospitalisations in Australia 2023–24 and the leading cause of injury deaths in 2022–23.
Seniors who have experienced a fall often develop a fear of falling again, which can lead to reduced physical activity and social isolation. This fear can create a vicious cycle, where decreased mobility leads to muscle weakness, further increasing the risk of future falls. Addressing fall prevention proactively can help break this cycle, fostering an environment where elderly adults feel secure and supported.
Common Causes of Falls in Elderly Adults
Falls in elderly adults often result from a combination of physical, lifestyle, and environmental factors. One of the most prevalent causes is decreased muscle strength and balance issues, which can stem from age-related changes in the musculoskeletal system.
As muscles weaken and joints become stiffer, maintaining stability becomes more challenging. This natural decline in physical capabilities makes elderly adults more susceptible to losing their balance and falling.
As vision gets worse, age-related eye conditions such as cataracts, glaucoma, and macular degeneration can significantly impair a senior’s ability to see obstacles and navigate their surroundings safely. Additionally, low lighting and glare can exacerbate visual difficulties, increasing the likelihood of stumbling or misjudging steps and uneven surfaces. Regular eye check-ups and proper lighting can help mitigate these risks.
Medications can also play a significant role in increasing fall risk. Many elderly adults take multiple medications, some of which may have side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, or low blood pressure. These side effects can impair balance and coordination, making falls more likely. Understanding the potential side effects of medications and consulting with healthcare providers to adjust dosages or explore alternatives can help manage this risk. Identifying and addressing these common causes is essential for effective fall prevention.

Assessing fall risk in the elderly
Assessing an elderly adult’s fall risk is an essential step in preventing falls. A comprehensive fall risk assessment involves evaluating various factors such as medical history, physical condition, and environmental hazards. Healthcare professionals often use standardized tools and questionnaires to identify individuals who are at higher risk of falling and these assessments can help tailor fall prevention strategies to the specific needs of each senior.
Physical assessments are a critical component of fall risk evaluation. Tests that measure balance, strength, and gait can provide valuable insights into a senior’s physical capabilities. For example, the Timed Up and Go (TUG) test, which involves timing how long it takes an individual to stand up from a chair, walk a short distance, turn around, and sit back down, can indicate potential mobility issues. Identifying physical vulnerabilities allows for targeted interventions such as strength and balance training exercises.
Environmental assessments are also crucial; identifying and mitigating hazards in the home, such as loose rugs, poor lighting, and clutter, can significantly reduce fall risk. Combining these assessments provides a holistic view of an individual’s fall risk and informs effective prevention strategies.
Home Safety Modifications to Reduce Fall Risks
Creating a safe home environment is one of the most effective ways to prevent falls in elderly adults. Simple modifications can make a significant difference in reducing hazards and enhancing safety to help mitigate the risk of serious injuries at home.
One of the first steps to make a space safer is decluttering. Removing unnecessary items, securing loose rugs, and organising furniture to create clear pathways can help prevent tripping and stumbling in older adults. It’s also beneficial to ensure that frequently used items are easily accessible to avoid the need for seniors to reach or climb.
Improving lighting throughout the home is another essential modification that can improve lifestyle overall. Adequate lighting helps seniors see potential obstacles and navigate their surroundings more safely. Things like brighter bulbs, using nightlights in hallways and bathrooms, and placing lamps near beds and chairs can add easy access and keep people safe.
Another key factor in home modifications is assistive devices. Things like grab bars in bathrooms, especially near toilets and showers, provide extra support and stability. Non-slip mats in the bathtub or shower and handrails on both sides of staircases can also prevent slips and falls. For those who are less mobile, installing a shower seat can also be a great option.
For seniors with mobility issues, raised toilet seats can also create a safer environment, allowing elderly adults to move around their homes with greater confidence and security.
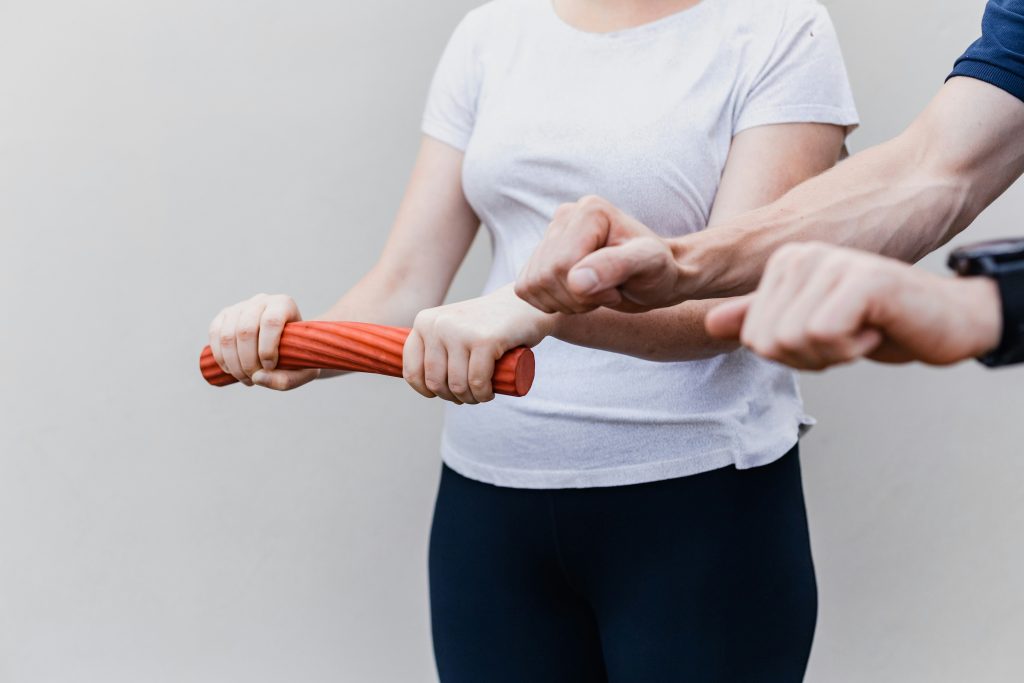
The Role of Exercise in Fall Prevention
Exercise helps improve muscle strength, balance, coordination, and flexibility, all of which are essential for maintaining stability and preventing falls. Strength training exercises, such as lifting weights or using resistance bands, can help build muscle mass and enhance overall body strength. No matter what your age, strength training helps people support their weight better and respond more effectively to potential balance disruptions.
Exercise physiology can be a crucial step for older adults who want to maintain muscle mass in later life and strengthen weak areas.
Checklist to limit the likelihood of falls:
- Get regular vision check ups
- Get regular overall health assessments
- Understand and manage any side effects from medication
- Ensure your home is free of tripping hazard and clutter-free
- Install home modifications that can aid movement
- Enlist the support of physio for preventative measures
How Physiotherapists Help Older Adults Prevent Falls
Physiotherapists work with seniors to strengthen their bodies, improve balance, and make their homes safer. Here’s how we do it:
- Assessing fall risk: Using simple tests for balance, walking, and strength, while checking for vision issues, medication side effects, or hazards at home.
- Targeted exercise programs: Strengthening the legs, improving posture, and boosting balance with proven methods.
- Gait and mobility training: Improving stride length, walking speed, and coordination, with or without a mobility aid.
- Mobility aids: Recommending and correctly fitting canes, walkers, or rollators — and teaching safe use.
- Home safety advice: Removing loose rugs, adding grab bars in bathrooms, improving lighting, and clearing pathways.
- Education and strategies: Teaching safe ways to move, turn, and get up after a fall, plus choosing supportive footwear.
- Post-fall recovery: Helping restore mobility, rebuild strength, and overcome the fear of falling to stay active and independent.
With the right physiotherapy support, older adults can feel stronger, more confident, and far less likely to experience a serious fall.